Industry 4.0: Is 5G the right Networking Technology?
5G is becoming the established wireless networking technology in many vertical applications in industry I4.0, ranging from energy, media, and transportation to digital society. Many industrial enterprises opt for a private network deployment using 4G LTE/LTE-A to support industrial enterprise key business drivers including (a) guaranteed and customized network SLA and KPIs (reliability, latency, availability, etc.), (b) controlled and secured coverage, and (c) strong security and privacy [1]. However, 5G delivers private and dedicated networks more effectively by means of hybrid network solutions that offer flexibility of both public and private networks, in a very dynamic environment, with different levels of isolation, sharing, and control to customize the network service towards particular industrial enterprise requirements. This in turn provides an economy of scale and globalization for I4.0 in terms of multi-domain networking solution, e.g. multi-site and multi-country, and thus reducing the total cost of ownership.
The figure below illustrates different 5G network deployment options, ranging from a public network to a fully standalone private network [1]. For example, it is possible to dedicate resources of the public network using 5G network slicing to create a virtualised private network to support I4.0 requirements including QoS/QoE, security and specific SLAs [2]; or allowing an operator to sublease their spectrum to enable a third party to build and manage a private network with a different level of management. With such rich deployment options, new network roles become possible such as Spectrum Licensee, (Virtual) Network Owner, Service Provider allowing to customize and automate the network service deployment at different levels. The decision of which network deployment option is better suited for a particular vertical will ultimately depend on the:
- Required level of isolation, sharing and control to customize the network service;
- Right balance between capital and operational expenditure;
- Capability of the enterprise to operate and control certain roles;
- Compatibility with the already existing infrastructure.

In addition to the flexible radio interface and network slicing capabilities, 5G networks are able to provide open networking solution creating opportunities for enterprises to reduce the total cost of ownership through horizontal multi-vendor integration while boosting innovation in vertical industries by means of open interfaces. With open networking, vertical industries could either plug-and-play a dedicated network on-premises and interconnect with a 3rd party services (e.g. edge computing or management subsystems), or mix-and-match different network components from different vendors to build or even deploy their custom network while exposing standardized open interfaces to allow operators to manage the network remotely.
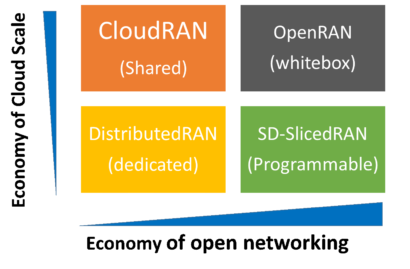
5G networks are unique in that they offer economy of cloud scale and open networking simplifying network management, integration or migration of existing data-system into a unified framework, and data processing and translation into actionable insights. In addition, 5G features mobility, reliability, scalability, security, low module cost, high device density, E2E application optimization and automation making it very attractive technology for current I4.0 as well as future I5.0.
[1] GSMA, 5G IoT Private & Dedicated Networks for Industry 4.0, 2020.
[2] R. Schmidt and N. Nikaein, Radio Access Network Slicing System, Wiley 5G Ref, 2020.

Navid Nikaein
Professor, Eurecom
Board Member, OpenAirInterface
Coordinator, Mosaic5G

R&D Engineer, Eurecom

Ph.D. Student, Eurecom